For the purpose of further adjustment of data on trade in goods of the balance of payment statistics of the Republic of Croatia with BPM6 methodology, the Croatian National Bank has set out to exclude, for the purposes of the balance of payment statistics of the RC, from goods imports and exports transactions not involving a change in ownership between residents and non-residents which are included in CBS trade in goods statistics, and to include in imports and exports transactions between residents and non-residents, taking place in the territory of the RC, which do not involve cross-border transfer of goods. The adjustment was made to the balance of payments goods account of the RC for all quarters of 2014, 2015 and 2016 and the revised data were released on 31 March 2017, together with the first data dissemination for the fourth quarter of 2016. Due to lack of reliable data required for previous periods data adjustment, the data on the balance of payments goods account of the RC for the second half of 2013 were not revised.
The revision made reduced the value of imports (debit on the goods account) and even more so the value of exports (credit on the goods account) recorded in the trade in goods statistics of the RC between 2014 and 2016. The possible reasons for these differences may be: 1) a time mismatch between the flow of goods, particularly the possible storing of the imported goods over longer periods of time prior to their exports and 2) differences in import (purchase) and export (sales) prices of goods crossing the territory of the RC. The latter has also been observed in other EU member states and has been described in an UN document Quasi transit trade in Europe: when value added does not belong to the reporting economy / Note by the Statistical Office of the European Union. It can mostly be attributed to costs of transport, storage and insurance of goods in circulation and to the system of transfer prices used by multinational companies to cut costs in international transit of goods through differences in tax and customs regulations in different countries.
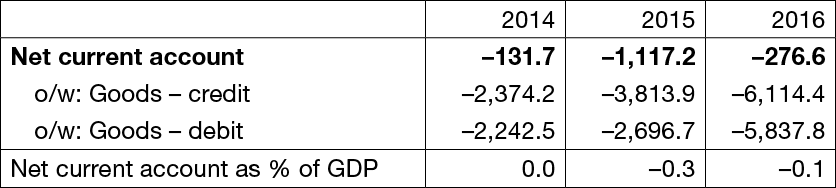
The impact of the revision on the already released data is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 The effect of adjustment on the balance of payments of the RC
in million HRK and as % of GDP-a
In the past, this methodological difference did not as a rule lead to differences in import and export data between the trade in goods statistics and the balance of payment statistics, with the exception of differences arising from the adjustment for coverage and classification of data on trade in goods from the trade in goods statistics, for the purposes of balance of payment statistics compilation which were also conducted earlier. This can be explained by a very limited possibility for non-resident imports into and exports from the RC prior to Croatia's accession to the EU. However, after 1 July 2013, the number and the value of transactions involving goods transfer across the border of the RC, not involving a change in ownership between residents and non-residents but involving a trade between non-residents, multiplied several times over. The accession of the RC to the EU meant that companies from all EU member states could operate freely in the RC. Based on a non-resident tax number (OIB), such companies may now import/export goods from/to all EU member states and trade with countries outside the EU, using the EORI number.
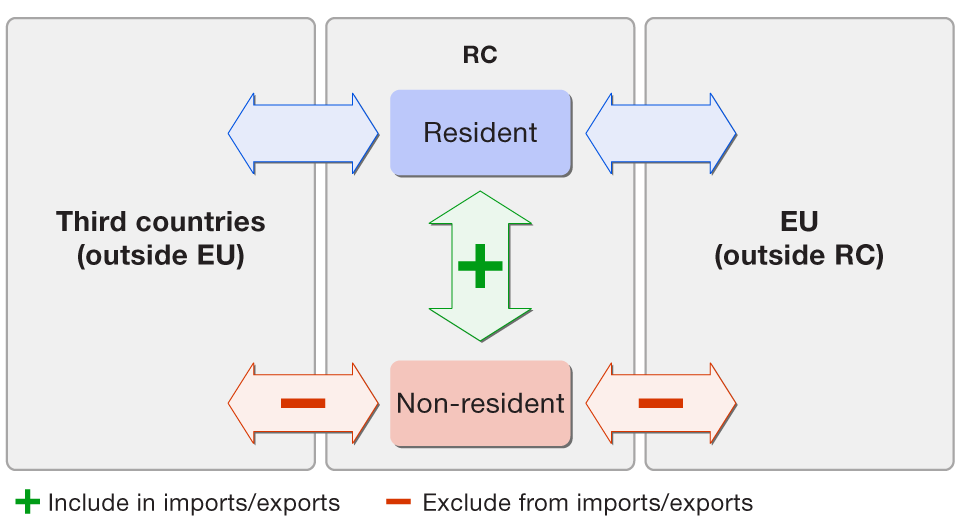
The statistics on the trade in goods of the Republic of Croatia compiled by the Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) defines goods imports and exports as each transfer of goods across the state borders of the RC, with the exception of goods in transit through the RC to other countries abroad (in which case the CBS does not include the value of such goods in imports or exports). At the same time, the balance of payment statistics of the RC compiled by the CNB, should include in goods imports (i.e. debit from trade in goods) and goods exports (i.e. credit from trade in goods) only transactions in goods which involve a change in the ownership of the goods between residents and non-residents of the RC, irrespective of the fact whether the goods have been transferred across the state border or not.
In the process of compilation of the trade in goods statistics of the balance of payments of the RC, the CNB will continue to adjust data on imports and exports from the trade in goods statistics of the RC by excluding cross-border transactions which do not involve a change in ownership between residents and non-residents and including trade in goods between residents and non-residents taking place in the territory of the RC. The necessity of this adjustment arises also from a recommendation issued by the European Commission (Eurostat) Foreign trade reported by non-residents, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Adjustment of the trade in goods data for the purposes of the balance of payment statistics of the RC