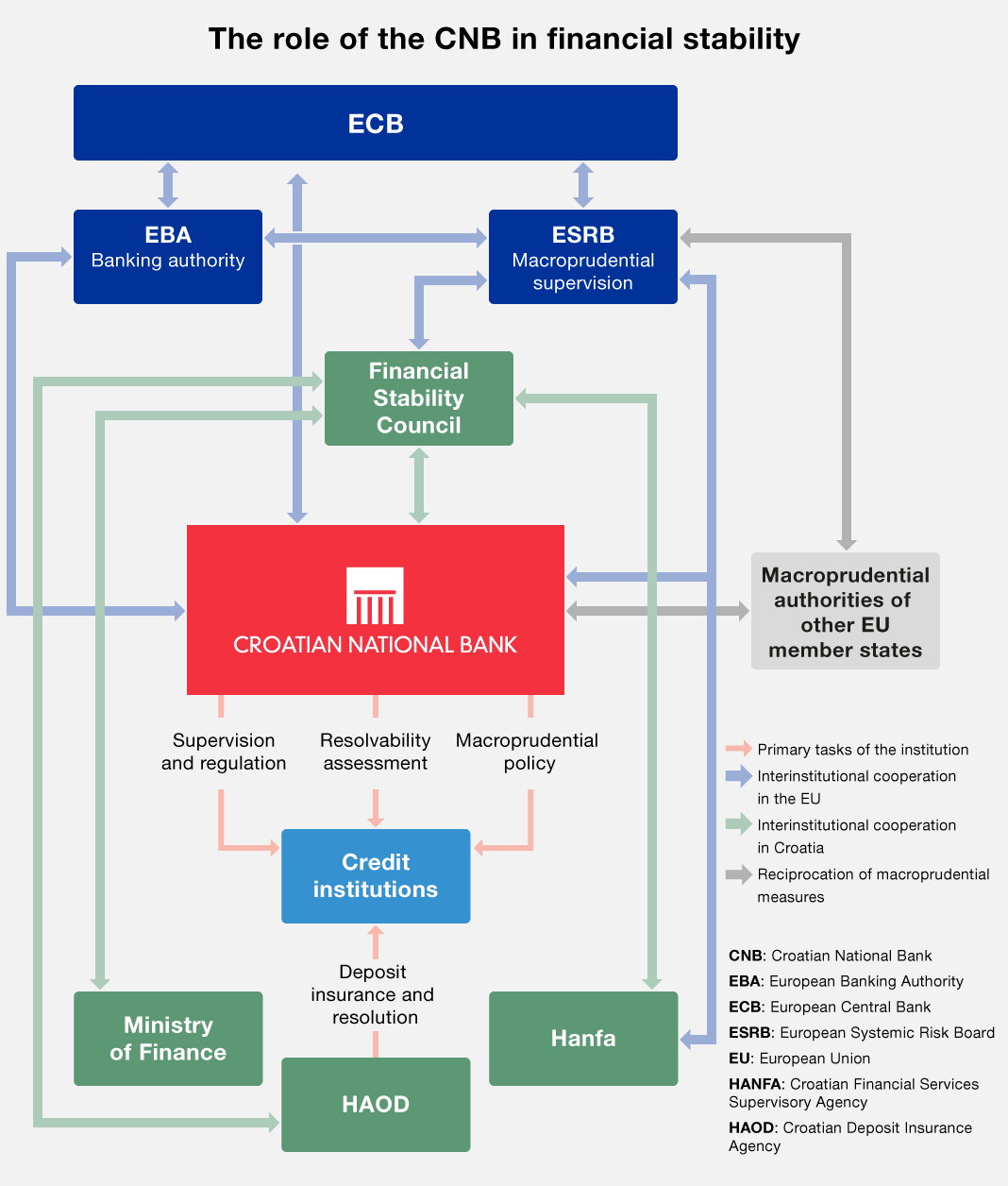
The Act on the Croatian National Bank, in addition to the main CNB's objective – maintenance of price stability, and monetary and foreign exchange stability, also lists among the principal CNB's tasks the contribution to the stability of the financial system as a whole. To that end, the CNB performs a systematic analysis of systemic risks that may threaten financial stability and adopts measures to prevent the emergence and spread of systemic risks, and to strengthen the resilience of the total financial system and thereby reduce the probability and costs of crisis episodes.
The main tasks of the central bank also include the regulation and supervision of banks with a view to maintaining the stability of the banking system, which dominates the financial system, as well as ensuring the stable functioning of the payment system.
Monetary and financial stability are closely related, for monetary stability, which the CNB attains by the operational implementation of monetary policy, performing the role of the bank of all banks and ensuring the smooth functioning of the payment system, lowers risks to financial stability. At the same time, financial stability contributes to the maintenance of monetary and macroeconomic stability by facilitating efficient monetary policy implementation.
Together with the Croatian Deposit Insurance Agency, the CNB is a resolution authority and is responsible for drawing up and updating resolution plans and for prescribing measures to remove impediments to resolvability.
Within the Financial Stability Council, the CNB cooperates closely with other authorities competent for regulation and supervision of non-banking financial institutions – Croatian Financial Services Supervisory Agency, the Ministry of Finance and the Croatian Deposit Insurance Agency.
Owing to the high degree to which the banking system is internationalised, as reflected in the foreign ownership of the largest banks, the CNB also cooperates closely with the home regulatory authorities and central banks of parent financial institutions.
Also important for the successful maintenance of financial stability in the country is cooperation with international institutions, in particular the European Central Bank and the European Systemic Risk Board, which is responsible for financial stability issues at the EU level.
Since the establishment of close cooperation with the European Central Bank on 1 October 2020, the Croatian National Bank has formulated and implemented macroprudential policy in cooperation and coordination with the European Central Bank.